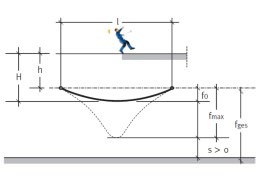
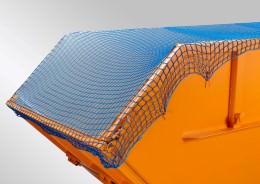
Main pageSafety Net Guidelines & Standards
Safety Net Guidelines & Standards
Construction Netting Guidelines
Guidelines For Other Safety Nets
Contact Us
- Schutznetze24 GmbH
Weyerberg 5
35614 Aßlar-Berghausen
GERMANY - +49 6443 - 436 96 40
![]() +49 6443 - 436 96 40
+49 6443 - 436 96 40- +49 6443 - 436 96 70
- office@safetynet365.com
Information
- Net Material Overview
- Assembly Instructions
- Building-Site Safety Netting Guidelines
- EN 1263-1 Safety Net Calculator
- FAQs
- Customer Images
- List of References
Useful Links
Bestseller
Custom-Made Netting
Nets for Home & Garden
Construction & Industry
Certifications
Awards
Accepted Payments
© 2026 Schutznetze24 GmbH • All Rights Reserved
modified eCommerce Shopsoftware © 2009-2026
modified eCommerce Shopsoftware © 2009-2026
Design: construktiv GmbH
Code & Implementation: Rehm Webdesign
Code & Implementation: Rehm Webdesign
safetynet365.com
- Customisation
- Construction
- Industry
- Load Securing
- Home & Garden
- Sport
- Information
- Contact
Contact Us
Monday - Thursday: 8:00 to 17:00
Friday: 8:00 to 12:00
Pickups and visits only with previous notice.
Friday: 8:00 to 12:00
Pickups and visits only with previous notice.
+49 6443 - 436 96 70
Schutznetze24 GmbH
Weyerberg 535614Aßlar-BerghausenHessenDE
+49 6443 4369640office@safetynet365.comhttps://safetynet365.com/templates/tpl_modified/img/logo/logo_head_en@2x.pnghttps://safetynet365.com/templates/tpl_modified/img/logo/logo_head_en@2x.png